TTL Expired in Transit :Reason and Solution: Have you ever received the vexing error message “TTL Expired in Transit” while attempting to access a website or send an email? Don’t be concerned; you’re not alone! Many internet users have been perplexed by this enigmatic error, leaving them scratching their heads. But don’t worry, we’re here to help you solve the riddle! In this blog post, we’ll delve deep into the meaning of TTL Expired in Transit, investigate various causes, and offer practical methods to overcome this stumbling block. So let’s get started and put a stop to this annoying problem once and for all!
Meaning of TTL Expired in Transit
Table of Contents



When you get the error message “TTL Expired in Transit,” it means that a time-to-live (TTL) value has expired when attempting to send data packets between servers. TTL is a countdown mechanism that networking devices use to decide how long data should be active or valid before being deleted.
The sender determines the TTL value, which is decremented at each network hop until it reaches zero. If there is a problem with routing or congestion, this mechanism ensures that data does not circulate indefinitely throughout the network. When the TTL expires, routers discard the packet and return an error message to the sender with the message “TTL Expired in Transit.”
This error often happens when there are router misconfigurations or network connectivity difficulties. It can also arise as a result of severe delays induced by heavy traffic, which causes packets to take longer than planned to arrive at their destination.
Understanding what “TTL Expired in Transit” means helps us understand why this problem occurs. Now, let’s look at some of the likely causes of this frustrating problem and work together to find effective remedies!
Understanding the TTL Expired in Transit Error



The TTL value of a network packet reduces by one with each hop via routers. If the TTL value becomes 0 at any stage, the router will drop the packet and return an ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) error message to the source.
This ICMP error is referred to as “TTL Expired in Transit,” and it alerts the sender that the packet did not arrive at its destination due to a low TTL value.
Possible Reasons for TTL Expired in Transit



When it comes to TTL expired in transit, there could be several causes for this problem. Let us look at some of the possible causes:
1. Network Congestion: Network congestion is a common cause of TTL expiration in transit. When the network is congested, packets may take longer to reach their destination and eventually perish.
2. Routing troubles: Routing troubles are another likely factor. Routers along the path may not have suitable routes configured or may be facing technical difficulties, resulting in packet drops and TTL expiration.
3. Firewall Restrictions: Firewalls are critical in safeguarding networks from unwanted access, but they can also interfere with packet flow at times. If a firewall is incorrectly setup or has severe rules in place, it may reject specific packets, causing them to expire.
4. Incorrect Time-to-Live Value: A packet’s Time-to-Live (TTL) value determines how long it can exist on the network before expiring. TTL expiration can occur if this value is set too low or if it is decremented several times along its travel owing to delays or loops.
5. Faulty Hardware: Faulty hardware, such as routers or switches, might contribute to TTL expired in transit errors in various instances. Malfunctioning equipment can result in packet loss or delays, which can lead to expiration.
6. Long-Distance Routes: Due to the greater likelihood of experiencing network difficulties such as latency and congestion along the way, packets traveling over long-distance routes are more vulnerable to TTL expiration.
When debugging TTL expired in transport problems, network administrators and IT professionals must identify and address these potential causes.
How to Solve TTL Expired in Transit?



In the world of networking, effective data transfer is critical for device-to-device communication. However, network packets can suffer faults along the way.
The “TTL Expired in Transit” error is a typical problem that can result in dropped packets before they reach their intended destination. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the nuances of TTL (Time To Live), investigate the causes of this mistake, and present step-by-step remedies to properly resolve it.
Clear Routing Tables: Clearing the routing tables on network devices can remove inaccurate or outdated entries, ensuring packets travel the best possible path.
Power Cycle Network Devices: Network devices may need to be restarted from time to time to refresh their routing information and eradicate any flaws that are generating the problem.
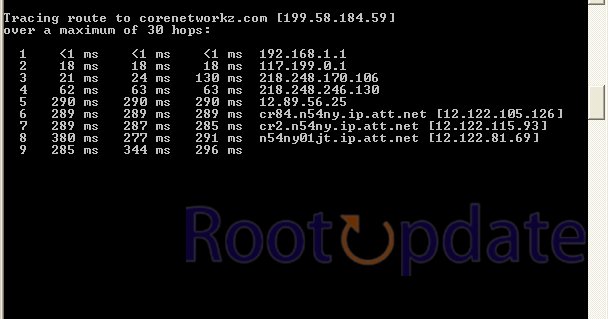
Use Tracert (Traceroute): Tracert (Traceroute) is a command-line utility that assists in tracing the path a packet takes to reach its destination. Users can identify the routers through which the packet goes and spot any potential difficulties by evaluating the data.
Check and Delete Wrong Entries: Manually inspecting and eliminating incorrect routing table entries can considerably enhance the packet’s chances of reaching its destination without experiencing the TTL issue.
Practical Example: Increasing TTL using Ping Parameter -i
Let’s look at how to use the ping argument -i to boost the TTL value. Assume we want to increase the TTL when pinging Google from 3 to 30 seconds.
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant Router
participant Google
User->>Router: ping -i 30 google.com
Router->>Google: (packet with TTL=30)
Google–>>Router: Response
Router–>>User: Response
In this example, pinging Google with the -i argument set to 30 results in a TTL of 30 for the packet transmitted to Google. However, because the TTL for the full route is insufficient, all four packets will face the TTL Expired in Transit error.
Other Similar ICMP Error Messages
Aside from the TTL Expired in Transit error, users may experience the following ICMP error signals during network communication:
Unreachable Destination Host: This error happens when the host or IP address given in the IP packet’s destination field is unavailable.
Destination Network Unreachable: This error message is displayed when the destination network is unavailable.
Request Timed Out: This error indicates that the network device or host failed to respond within the time limit given.
The Remote Computer Did Not Respond: Error 678 This error, which is commonly encountered in dial-up connections, indicates an issue with the distant computer’s answer.
Related:
- Download Miracle Box Setup Tool without Box v3.32 (2024)
- Canva Pro Edu Team Invite Link For Free August 2024
Conclusion
TTL expired in transit is a typical problem that occurs when data packets do not arrive at their destination within the set time frame. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including network congestion, incorrectly configured routers, or erroneous TTL values specified on the packets.
It is critical to identify and address the root source of this problem in order to resolve it. This could entail fixing network connectivity difficulties, modifying routing setups, or altering TTL values to improve packet delivery.
It is also critical to regularly check and adjust your network infrastructure to avoid TTL expired in transport problems. You can ensure seamless data transmission and reduce disruptions for your users by keeping an eye on your network performance and making appropriate adjustments.
It is important to remember that fixing TTL expired in transport problems necessitates technical knowledge and skills. If you are unsure how to handle this problem or if it persists despite your efforts, consider seeking help from a knowledgeable IT specialist who can successfully diagnose and resolve the problem.
Understanding the meaning of TTL expired in transport, identifying alternative reasons, and implementing relevant remedies will prepare you to manage this common networking quandary with ease.
So, the next time you get a TTL expired in transit error message or receive user complains about slow connections or failed requests, don’t panic! Take a methodical approach to discovering and resolving the underlying issues that are creating the problem. You’ll be able to keep your network working smoothly and deliver uninterrupted services to your users if you have patience and perseverance.