Change the Default Size of Ping Echo Request On Your Computer: Welcome to computer networking, where every bit counts! If you’re a techie who enjoys delving into the nuances of internet connections, you’ve probably come across the infamous “ping” command. This useful application calculates the time it takes data packets to transit from your computer to another device on a network. But did you know that you may change the default size of this ping command to adjust and optimize it?
In this blog post, we’ll look at how to use the “ping -l” command to adjust the default size of ping echo requests on your machine. We’ll explain why this change is necessary, present a step-by-step guidance for making it, explore potential consequences, offer troubleshooting advice, and finally empower you with greater knowledge in navigating the huge universe of networking.
So take your metaphorical toolbox and join us as we embark on an exciting trip to customize the size of your ping echo request – let’s get started!
Understanding the Default Size of Ping Echo Request
Table of Contents



The ping command is a useful tool for debugging network connectivity difficulties. You can test your connection by sending echo request packets to a certain destination and measuring the response time. But have you ever considered the standard size of these echo request packets?
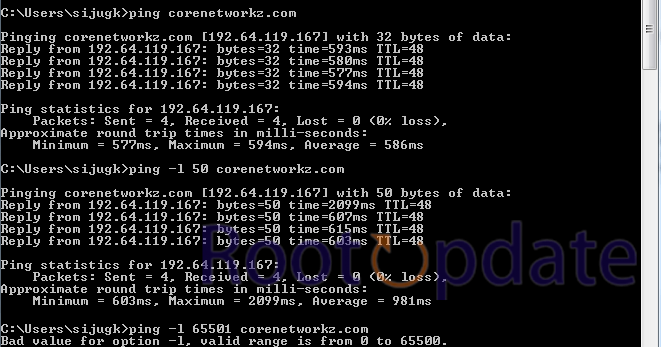
When you execute the ping command without any further options, it sends 32 bytes of data in each packet by default. This implies that your computer sends out little amounts of data with each ping request and waits for a response from the target device or IP address.
But why is the default size so significant? Smaller packet sizes, on the other hand, are often more suited for evaluating basic connectivity because they use less bandwidth. Larger packet sizes, on the other hand, can aid in the detection of problems associated with fragmented or overcrowded networks.
It may be essential to adjust the default size of the ping echo request packets to gain a fuller picture of your network’s capabilities and performance under varied conditions.
Importance of Changing the Ping Echo Request Size



The ping command is a commonly used tool for debugging network connectivity difficulties. This command transmits a tiny packet of data known as an echo request to a certain IP address or domain name and timers the response, known as the echo reply. This packet size is set to 32 bytes by default.
However, in some cases, adjusting the default size of the ping echo request is critical. One example is when you need to test network performance with larger data packets. You can mimic real-world events and uncover potential bottlenecks in your network infrastructure by increasing the size.
Another reason why adjusting the ping echo request size might be useful is for debugging. Certain firewalls or routers may occasionally block ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) communication based on packet size. By permitting or restricting specific ping packet sizes, you may detect if these devices are creating any problems.
Changing the ping echo request size can also aid in the testing of Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your network equipment. QoS aids in the prioritization of some types of traffic over others, ensuring maximum performance for key applications such as VoIP or video streaming. You can determine whether QoS regulations are correctly installed and performing as intended by delivering bigger packets during a ping test.
While most users are unlikely to need to adjust the default size of their ping echo requests on a frequent basis, recognizing its significance can be useful in certain scenarios. The ability to alter this parameter provides flexibility and insight into the behavior of your network infrastructure, whether it’s measuring network performance with larger data packets or resolving firewall limits and QoS settings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Change the Default Size of Ping Echo Request On Your Computer



To change the ICMP echo request packet size, follow these simple steps:
- Open the command prompt or terminal on your device.
- Use the following format for the “ping” command:
ping -l (value between 0 to 65500) [Destination Address]Replace
(value between 0 to 65500)with the desired packet size in bytes, and[Destination Address]with the target IP address or domain name. - Press Enter to execute the command.
- Observe the output to see if the target destination responds to the modified packet size.
Potential Impacts of Changing the Ping Echo Request Size
When it comes to adjusting the default size of a ping echo request on your computer, you should be aware of certain potential consequences. While changing the packet size may appear to be a little tweak, it can have a significant impact on your network and connectivity.
One possible consequence is higher network load. You are simply sending larger data packets across your network by increasing the packet size. This can result in increased bandwidth utilization and potentially slower response times for other network-connected devices.
Furthermore, increasing the ping echo request size may result in erroneous latency results. Ping is frequently used to determine the round-trip time or latency between two devices. However, if you considerably change the packet size, it may not correctly reflect real-world situations and can bias your results.
Furthermore, some firewalls or security settings may process larger packets differently than smaller packets. Any firewall restrictions or security measures in place should be considered since they may interfere with the appropriate transmission and receiving of modified ping packets.
Changes to the default ping echo request size will not necessarily increase overall performance or speed up your internet connection. It’s critical to note that this change just changes how ping works and has no effect on other aspects of network performance.
Related:
- Fix: TTL Expired in Transit :Reason and Solution
- Ping Request Could Not Find Host. Please Check the Name and Try again
- Enable Google SafeSearch Lock Permanently On Firefox, Chrome etc
Conclusion
In this blog post, we looked at how to use the “ping -l” command to change the default size of ping echo requests on your machine. You may improve your network troubleshooting and gain more control over your pinging operations by learning how to change the packet size.
Changes to the ping echo request size should be done with caution, since they may have an influence on network performance and cause significant problems. Before making any changes, it is critical to consider considerations such as bandwidth constraints and network congestion.
You may easily alter the packet size to meet your specific needs by following our step-by-step guide. Keep in mind, however, that changing this option may not always result in considerable improvements or fix all networking problems.
If you have any problems or unexpected results when altering the ping echo request size, please refer to our troubleshooting instructions for assistance.
The ability to adjust the default size of ping echo queries provides you more control over your network connections. Knowing how to change this parameter can improve your general computing experience, whether for diagnostic purposes or to optimize performance in online gaming or streaming applications.
So go ahead and experiment with different packet sizes while keeping an eye on how they affect performance. With a little practice and experimentation, you’ll be able to properly change this setting.
We hope you found this post interesting and helpful in determining how to change the default size of ping echo requests on your computer. Have fun pinging!